Introduction
Manufacturing overheads affect companies in many different—and inescapable—ways. Cost management, pricing strategies, profitability analysis, and investment decisions are all important elements that are intrinsically tied into manufacturing overheads.
In addition to these, your company's competitiveness, financial reporting, cash flow management, cost reduction initiatives, and ultimate customer satisfaction will all be brought to light when looking at this all-important company process. It therefore merits a closer look, so here’s a detailed breakdown on how to manage the process effectively.
To see more about Cost of Goods check: Cost of Goods Manufactured
How Overhead Costs are Distributed?
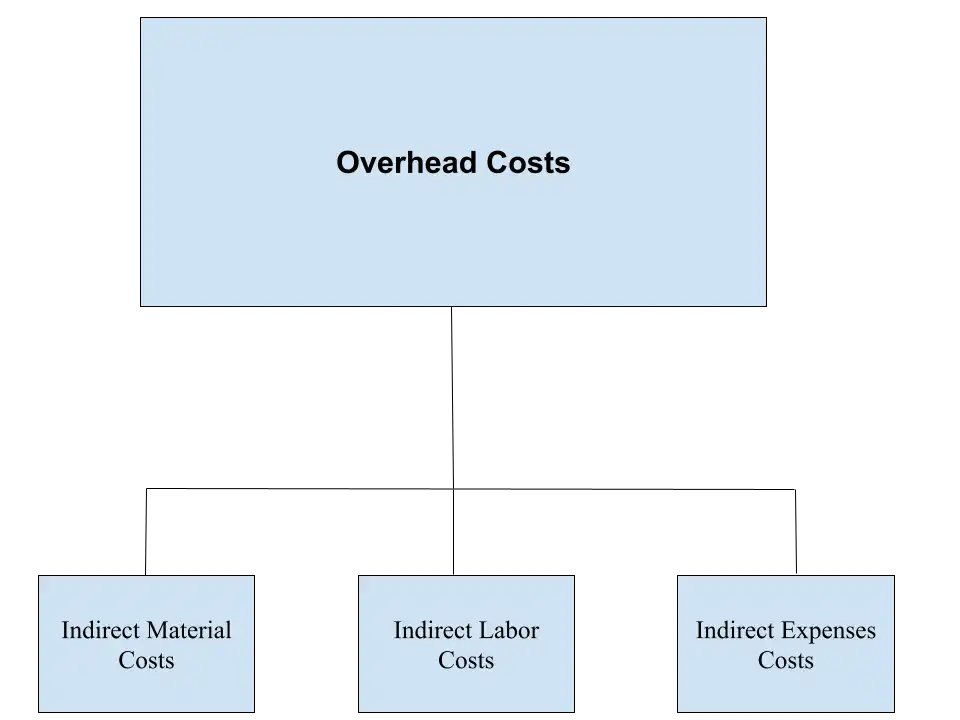
Overhead costs must be tracked in order to verify which indirect costs are imposed on the manufacturing of any product, and with Odoo it’s possible to do this seamlessly. Various adjustments may occasionally be necessary for various reasons, like changes in the production volume, unexpected expenses, or revisions to the company’s overhead allocation methods.
By making these adjustments, companies can ensure that the costs attributed to the manufacturing of each product are as accurate as possible. Why is this important? Well, it helps you to accurately determine overall product costs, as well as evaluate profitability and pricing. The ability to adjust your overhead costs is a powerful tool that affects much of your business reporting, so let’s look at how this can be done.
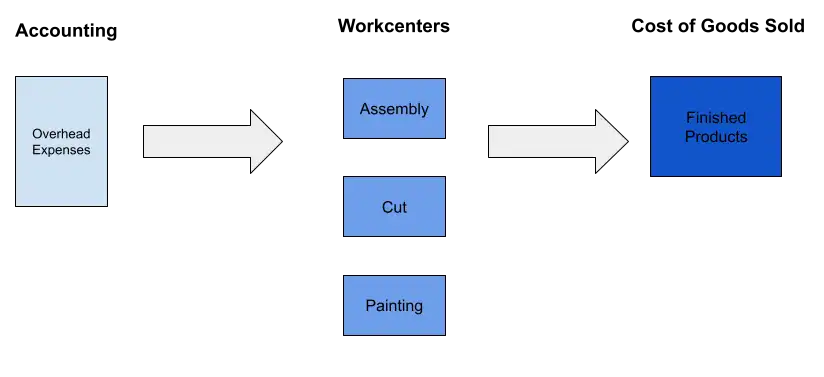
How to Adjust Your Manufacturing Overheads
Here’s a hypothetical example of a manufacturer specializing in dinner tables who plans to sell 80 units at a unit price of $520. Each Table takes 1 hour to make and has a production cost of $260. To break down this cost, we notice:
- Raw Materials ⇒ Table Top (1 unit x $100) ⇒ Legs (4 units x $25)
- Overhead Costs ⇒ 1 hour x $60 (estimated), assuming it's just one workcenter called a wood shop.
In this example, the manufacturing overhead costs include depreciation of equipment, salary and wages paid to factory personnel, and electricity used to operate the equipment.
The company has estimated these as the expenditures it will incur during the manufacturing process of one product. After doing the sale, a purchase will be activated to buy the Table Tops (1 x $100 x 80=$8,000) and the Legs (4 x $25 x 80=$8,000) to then manufacture the tables. Once these products are received, Odoo automatically creates these journal items to provide a helpful overview.
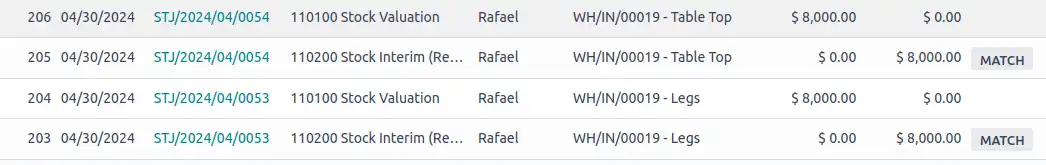
In this case Odoo automatically moves the Purchase Value to Stock Valuation. To check these moves you need to go to the Accounting Module and click Accounting before selecting the Journal Entries. It’s always possible to check the journal entries in every step of your transactions.
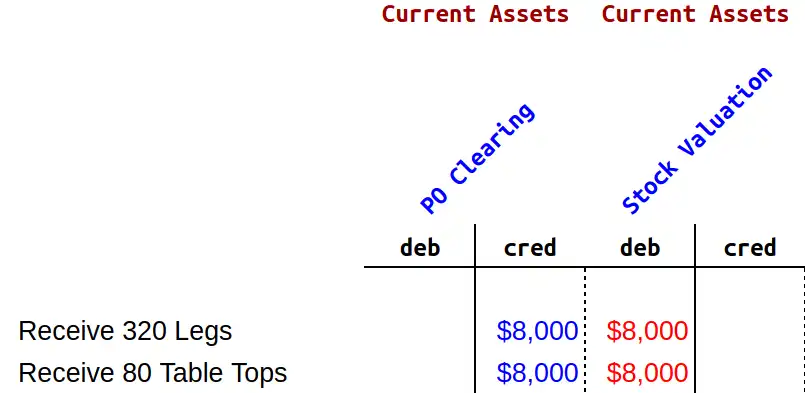
If we evaluate this process in T accounts, we can see that the moves are exactly the same.
Upon receipt of these products, the subsequent stage involves the payment of the raw materials and the table manufacturing. Once the work order is completed, Odoo seamlessly transfers the Stock Valuation to Production Cost Stock.
As you can see in the image below, the cost of the dinner table per unit is $260; with the raw materials having a cost of $200 and the cost of operations $60. With Odoo v.17, there is a feature that allows us to also input the employee cost included in the operations (here we assume $0).
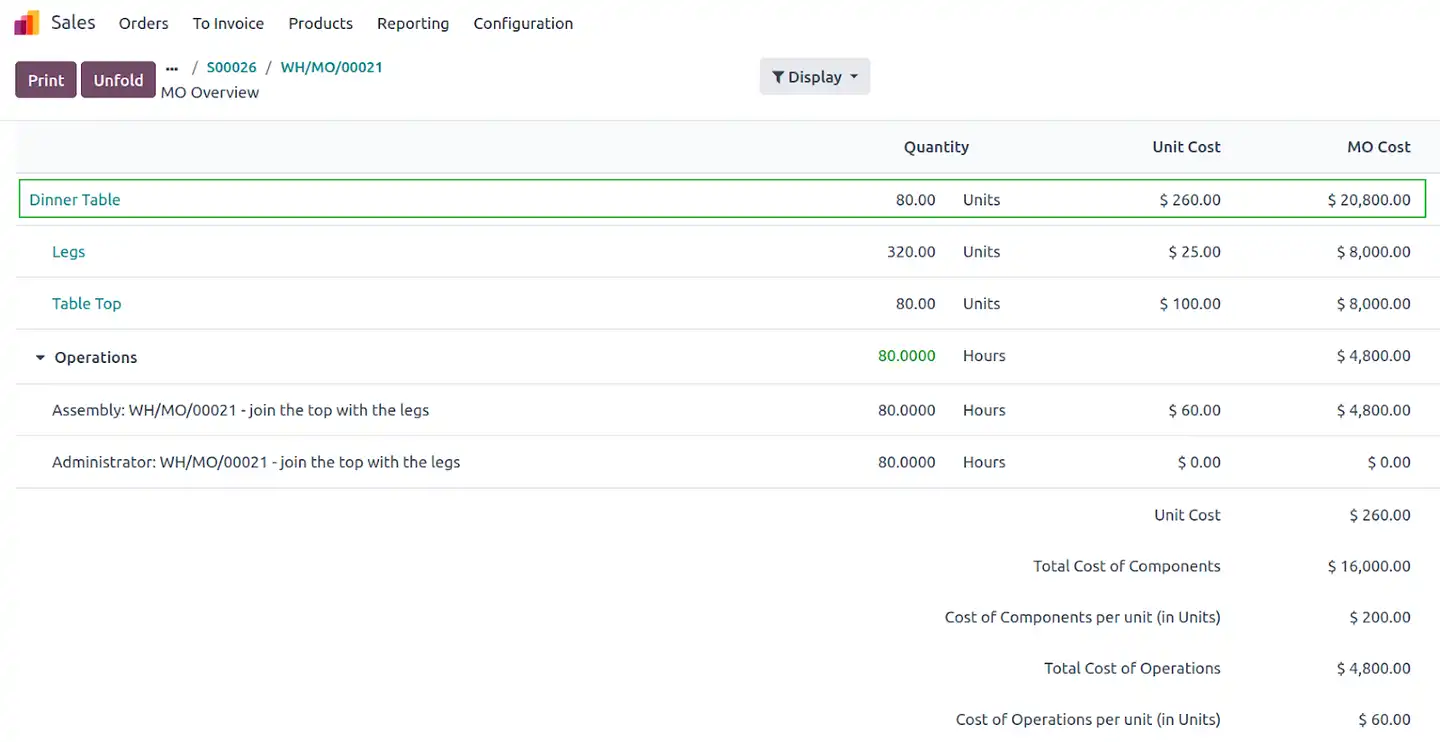
So the Total Cost of the 80 Dinner Tables is: ⇒ $20,800 = $16,000 (Cost of Components) + $4,800 (Cost of Operations).
After producing the Tables, the next steps are shipping, invoicing, and receiving the payment from the client. These steps generate the moves depicted in the image below:
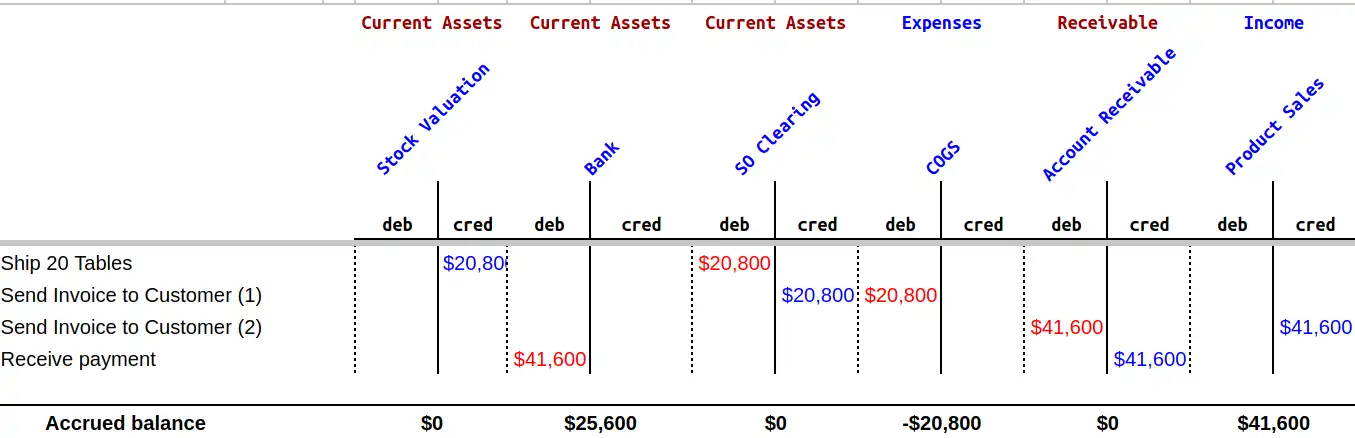
As said before, if each Table will be sold for $520, then the total payment that should be received is $520 x 80 units = $41,600.
Now imagine that at the end of the period, we will collect the real overhead costs from vendor bills, equipment depreciation, or wherever they may come from: Overhead Costs ⇒ Direct Labour: $6,000 ⇒ Electricity Bill: $1,500 ⇒ Depreciation: $650
= Total: $8,150
In this case there's a discrepancy between the estimated costs ($4,800) and the actual costs ($8,150). $4,800 - $8,150 = $3,350
So, at the end of each accounting period, it’s mandatory to make an adjustment:
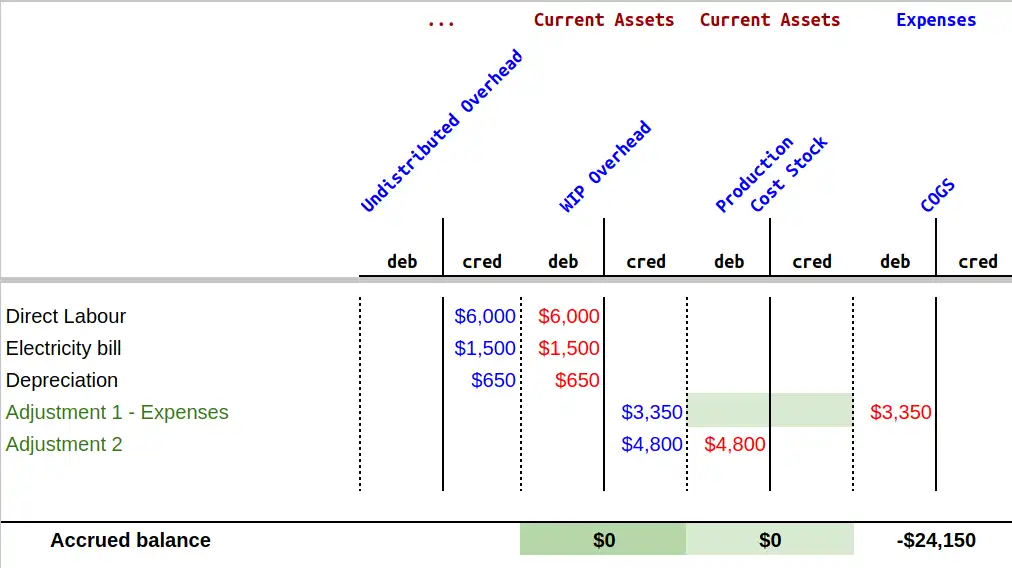
Note: The undistributed Overhead Costs (Direct Labour, Electricity Bill, Depreciation) are separated accounts, so the information has been presented like this for a better visual perception of their transition to the wip overhead account. In the image above, the Direct Labour, the Electricity Bill, and Depreciating Real Values are credited from the Undistributed Overhead account. They will therefore be debited on the Wip Overhead account.
To settle this account we must credit the $3,350 (the difference between the real overhead costs and the predicted ones) and the $4,800 (the predicted overhead costs). After this, the $4,800 must be removed from the Production Cost Stock by debiting the account. The $3,350 should therefore be debited in Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) because that’s the difference between the predicted costs and the actual costs.
After these adjustments, the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is $24,150. This means that the cost of the products is $16,000 (cost of components) plus $8,150 (real overhead cost). The workcenter cost must be changed after knowing the real overhead costs. In this case as we see that ultimately, the total overhead costs are $8,150. Keeping in mind that the company has produced 80 Dinner tables, the necessary calculation to make is as follows:
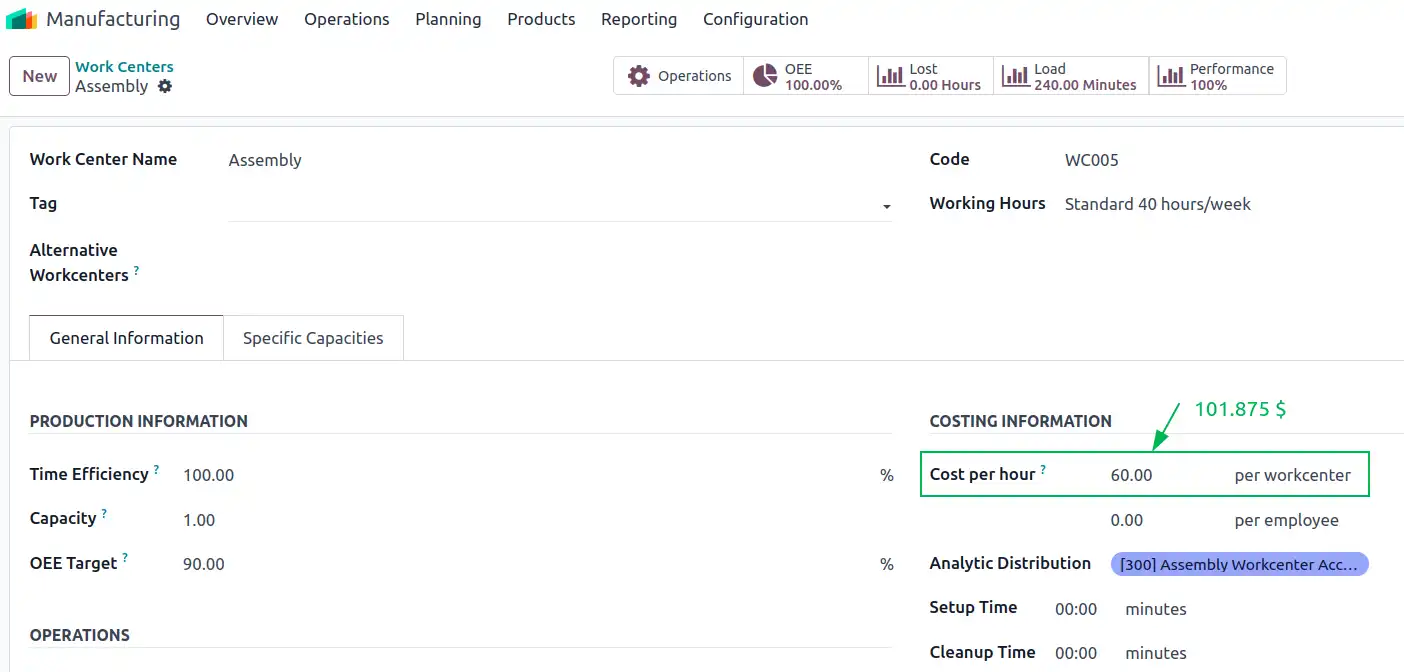
$8,150 / 80= $101,875 per hour
To change this value in Odoo, we simply go to the Manufacturing module and then to Configuration>Work Centers. From here you can easily select the Work Center you want to change. After this, the cost per hour must also be changed; in this case we change it from $60 per hour to $101.88 per hour.
Conclusion
Manufacturing overheads management is a crucial aspect to ensure the efficiency and profitability of manufacturing operations. Odoo helps businesses with the manufacturing module, tracking, allocation, and analyzing of the overhead costs. This makes it possible to make more informed decisions and strive for improved profitability.
Using Odoo’s capabilities empowers organizations to navigate the intricate landscape of overhead management with accuracy and efficiency, positioning them for long-lasting success in an ever-evolving marketplace. If you’re looking to trim overhead costs without the hassle, our team of consultants can help. So let's discuss how to optimize your resources for maximum efficiency.
Reach out today to learn more!
Follow Us on Social Media
Stay connected with ERPGAP and follow us on this journey. You can view updates on LinkedIn and Twitter.



